Algeria Country Fact About
Information about the country of Algeria
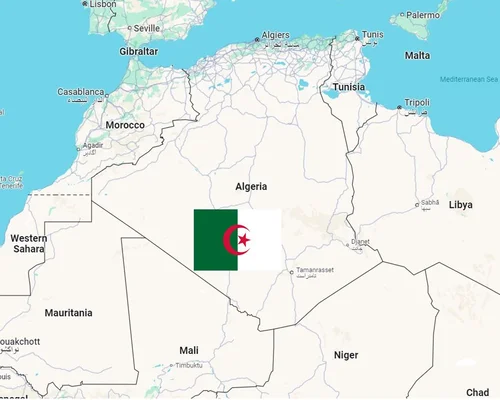
Algeria is a country in North Africa and the largest country in Africa.
Here are some important facts about Algeria:
1. Geographic Information:
Location: Algeria is located in North Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea on its northern border and neighboring countries are Tunisia, Libya, Niger, Mali, Mauritania, Western Sahara and Morocco.
Capital: The capital of Algeria is Algiers, located on the Mediterranean coast.
Size: Algeria is the largest country in Africa and the tenth largest in the world.
Topography: Most of Algeria is covered by the Sahara desert, which covers about 80% of the country. There are also mountains and beaches.
2. Population:
Population: As of 2024, the total population of Algeria is about 45 million.
Ethnic Groups: The majority of the country population is Arab-Berber. The Berber population especially came from the Kabyle region.
Language: Arabic is the official language of Algeria. In addition, Tamajigat (Berber language) was recognized as an official language in 2016. French is also widely spoken in Algeria, as it was once a French colony.
3. Government and Politics:
Government: Algeria is a republic, where the president is the head. President is elected for 5 years.
Independence: Algeria gained independence from France on July 5, 1962. There was a war of independence from 1954 to 1962, which was extremely bloody.
Political parties: Algerian politics is still dominated by the National Liberation Front (FLN) party, which played an important role in the struggle for independence.
4. Economy:
Currency: The official currency of Algeria is the Algerian Dinar (DZD).
Natural Resources: Algeria is rich in mineral resources, especially oil and natural gas. It is one of the world leading natural gas producers and one of the main gas suppliers in Europe.
Economy: Algeria economy is mainly dependent on hydrocarbon (oil and gas) exports. About 90% of revenue comes from oil and gas exports.
5. Culture:
Religion: Almost the entire population of Algeria is Muslim and it is the official religion of the country.
Food: Couscous, tajine, and bric are among the most popular Algerian dishes. Olive oil, spices and dates are used in cooking here.
Music and Art: Algeria is famous for Rai music, which is one of the country most popular music genres. Berber and Arab-Andalusian music also plays an important role in the country culture.
6. History:
Colonial History: France occupied Algeria in 1830 and remained a French colony for over 130 years. The War of Independence took place between 1954 and 1962, one of the most violent anti-colonial struggles of the 20th century.
Battle of Algiers: The Battle of Algiers in 1956-57 was an important chapter in the struggle for independence.
7. Tourism:
Tourist places: Algeria has several UNESCO World Heritage sites, such as the ancient Roman city of Timgad, the Mojab Valley, and the Kasbah of Algiers. Besides, the Sahara desert is very popular among travelers.
Tourism development: Although Algeria is rich in natural beauty and heritage, the tourism sector is not as developed as in other North African countries, partly due to security concerns.
8. Major Challenges:
Unemployment: Unemployment among the youth is a major problem, even though the educated population of the country is high.
Political protest: The Hirak movement, which began in 2019, brought significant changes to Algeria political scene. As a result of this movement, longtime president Abdelaziz Bouteflika resigned.
9. Flag:
The flag of Algeria has two colors, a green and white. Green symbolizes Islam and white symbolizes peace. In the center of the flag is a red moon and star, which is used as a symbol of Islam.
10. Weather:
Algeria coastal areas have a Mediterranean climate, with rainy winters and hot summers. However, the Sahara desert region has an extreme climate with a mixture of warm days and cool nights.
Algeria is one of the most important countries in North Africa for its natural resources, cultural heritage and rich history.