Ecuador Country Facts
Ecuador Country Facts
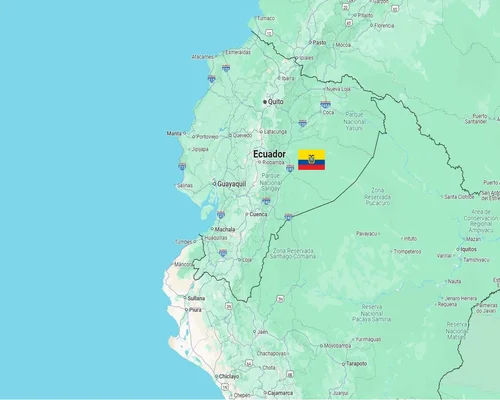
Ecuador is a small but diverse country in South America, known for its vibrant culture, the Galapagos Islands, and the Andes Mountains. Its name comes from the Equator, as the equator passes through the country.
General Information:
Capital: Quito.
Largest City: Guayaquil.
Location: Located in the northwestern part of South America. Bordered by Colombia to the north, Peru to the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west.
Area: 283,561 square kilometers.
Population: Approximately 18 million (2024 estimate).
Government:
Democratic republic. The president is the head of state and head of government.
Language: Spanish (official language). Some indigenous languages are also spoken, such as Quechua.
Currency: United States dollar (USD).
Independence: Gained independence from Spain on May 24, 1822.
Geography and climate:
Natural features: Ecuador is divided into three geographical regions:
Costa (coastal region).
Sierra (Andes Mountains).
Oriente (Amazon rainforest).
Galapagos Islands.
Highest peak: Chimborazo: 6,263 meters above sea level.
Equator: Ecuador has a monument to the equator called Mitad del Mundo.
Climate: Tropical, but varies by region. Cool in the Andes, warm on the coast, and humid in the Amazon.
Economy:
Main Sector: Oil extraction is the main sector of Ecuador economy. Agriculture, especially bananas, cocoa, and flowers, is the country main industry.
Tourism: Tourism plays an important role in Ecuador economy due to the Galápagos Islands.
Industry: Oil refining, food processing, and the clothing industry.
History:
Prehistoric times: Ecuador was ruled by the ancient indigenous peoples of the Quichua and Incas.
Spanish colonization: Ecuador was conquered by Spain in 1533. Quito was an important city in the Spanish Empire.
Independence: In 1822, it gained independence under the leadership of Simón Bolívar.
Culture and lifestyle:
Religion: Primarily Roman Catholic. Religious freedom exists in modern society.
Language and literature: Ecuador has a rich literature, including works by Jorge Icardi Carreño and Alfredo Pérez.
Food:
Popular dishes:
Ceviche: a seafood dish.
Locro de papas: Potato soup.
Encebollado: Fish and onion soup.
Music and dance:
Pasillo and pascal occupy a special place in Ecuadorian music and folk dance.
Environment and biodiversity:
Biodiversity hotspots: The Galapagos Islands are one of the world centers of biodiversity. The Galapagos Islands inspired Charles Darwin theory of evolution.
National parks:
Yasuni National Park: Part of the Amazon rainforest and important for biodiversity.
Special places:
The Galapagos Islands: A UNESCO World Heritage Site for its unique fauna and natural environment.
Quito city: Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site for its ancient architecture.
Chimborazo mountain: The highest point from the center of the Earth.
Challenges and the future:
Challenges: Economic inequality and poverty.
Environmental issues, especially the impact of oil extraction.
Development plans: Sustainable tourism development and environmental protection. Investment in renewable energy.
Conclusion:
Ecuador is one of the most important countries in South America for its natural beauty, cultural diversity, and historical importance. The Galapagos Islands and its location on the equator make the country very attractive to tourists.