Dominican Republic Country Fact
Dominican Republic Country Information
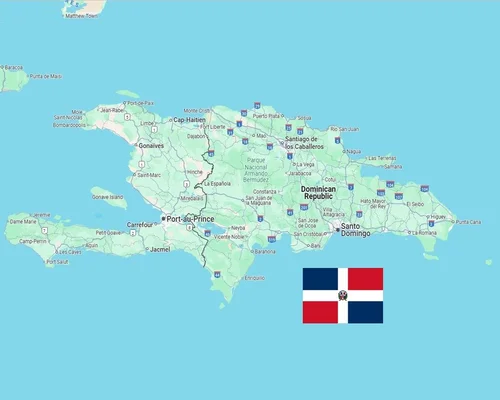
The Dominican Republic is an island country in the Caribbean, known for its beaches, mountains, rich culture, and tourism. It is located on the eastern part of the island of Hispaniola, with Haiti on the western part of the island.
General Information:
Capital:
Santo Domingo.
Location:
Located on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea.
The Atlantic Ocean to the north and east, the Caribbean Sea to the south, and Haiti to the west.
Area:
48,442 square kilometers.
Population:
About 11 million (2024 data).
Government:
Democratic republic.
The president is the head of state and head of government.
Language:
Spanish (official language).
Currency:
Dominican peso (DOP).
Independence:
Won independence from Haiti on February 27, 1844.
History:
Ancient times:
The Taíno people were the first inhabitants of the region.
In 1492, Christopher Columbus discovered the island of Hispaniola.
Colonial period:
The island became known as the first colony of Spain.
It later underwent changes of power between France, Haiti, and Spain.
Independence movement:
It became an independent country after gaining independence from Haiti in 1844.
Geography and climate:
Natural features:
The Dominican Republic has mountains, plains, and coastal beaches.
Highest peak:
Pico Duarte: The highest mountain in the Caribbean, at 3,098 meters.
Climate:
Tropical climate.
Hot and humid most of the year.
Special places:
Puerto Plata: Famous for its beaches and tourism.
Samaná Peninsula: Popular for whale watching.
Economy:
Main sectors:
Tourism, agriculture, and mining.
Tourism is the main driver of the Dominican economy.
Agriculture:
Main agricultural products: sugar, coffee, cocoa, and bananas.
Industry:
The country is notable for its production of ready-made garments, cigars, and electronic products.
Special income:
A large part of the country income comes from remittances (money sent by expatriates).
Culture and tradition:
Religion:
Primarily Roman Catholic.
Some areas have Protestant and other religious influences.
Festivals:
Dominican Carnival: Held in February.
Merengue Festival: Celebrated in honor of the country traditional music, merengue.
Food:
Popular dishes: Las banderas (rice, beans, and meat), sancocho (meat stew), and tostones (fried plantains).
Sports:
Baseball is the most popular sport in the Dominican Republic.
The country is home to many famous baseball players.
Environment and Biodiversity:
Plants and Animals:
The Dominican Republic has a diverse biodiversity.
Many species are found only in this region.
Nature Reserves:
Parque del Este: An important nature reserve.
Laguna de Oviedo: Famous for its flamingos and other birds.
Special Features:
Geographical Importance:
It is one of the largest tourist destinations in the Caribbean.
Cultural Diversity:
The blend of Spanish, African, and Taino cultures has enriched Dominican society.
Food and Music:
Merengue and Bachata music are a large part of the country cultural life.
Challenges and Future:
Challenges:
The impact of hurricanes and climate change.
Poverty and income inequality.
Development:
Plans are being made to increase economic growth through sustainable tourism and infrastructure development.
Conclusion:
The Dominican Republic is popular around the world for its beaches, natural beauty, and cultural heritage. Its success in tourism and agriculture has established the country as one of the most important economic centers in the Caribbean.