Facts about Benin
Facts about Benin
Benin is a small but historically and culturally diverse country in West Africa. It is known for its history of the ancient Dahomey kingdom and its modern development efforts. Below are some important facts about Benin:
Geographical location:
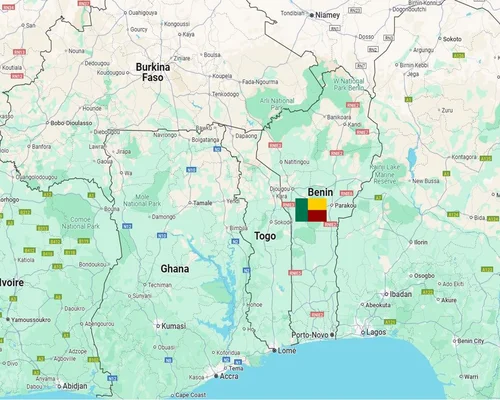
Location:
Coastal country in West Africa.
It stretches from north to south in a long line.
Borders:
To the north: Burkina Faso and Niger.
To the east: Nigeria.
To the west: Togo.
To the south: Gulf of Guinea.
Capital and major cities:
Capital: Porto-Novo.
It is the administrative capital.
Largest city: Cotonou.
It is the commercial center and the country principal city.
Other cities: Abomey, Parakou, Natitingou.
Population and languages:
Population: About 13 million (as of 2024).
Language:
Official language: French.
Local languages: Fon, Yoruba, and other indigenous languages.
History:
Dahomey Kingdom:
A powerful kingdom founded in the 17th century.
Dahomey female warrior army, the "Amazons", is famous.
Colonialism:
Came under French rule in 1894.
Gained independence in 1960.
Name change:
After independence, it was known as Dahomey.
The name was changed to Benin in 1975.
Economy:
Agriculture:
The country main economic sector.
Cotton, cassava, and almonds are among the main crops.
Tourism:
Historical sites, the Dahomey royal palace, and the slave trade history of Ouidah attract tourists.
Trade:
The port of Cotonou is the country main commercial center.
Religion:
Main religion:
Christian (about 48%).
Muslim (about 27%).
Traditional religion:
Benin Vodun: Vodun originated in Benin and is a part of its heritage.
Culture:
Music and dance:
Traditional drum music and dance are world-famous.
Handicrafts:
Wood and bronze crafts are one of Benin specialties.
Festivals:
Voodoo Festival: Celebrated on January 10 and is internationally known.
Natural beauty:
National parks:
Pendjari National Park and W National Park.
These include wildlife such as elephants, lions, and cheetahs.
Lake Nkowe:
Home to the traditional floating village of Ganvie.
Education and health:
Education:
Education is compulsory, but still needs to improve.
Health:
Malaria and other infectious diseases are a problem.
Conclusion:
Benin is a country rich in history, culture, and heritage. The palaces of Dahomey, the main centers of Voodoo religion, and natural resources make Benin unique in the world. Although it is a developing country, its cultural heritage and historical importance are internationally recognized.