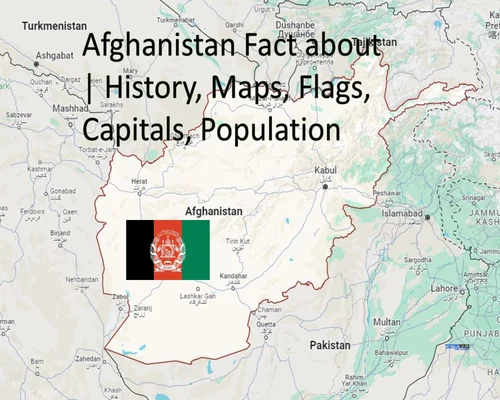
Afghanistan Fact about History, Maps, Flags, Capitals, Population
Afghanistan Fact about History, Maps, Flags, Capitals, Population
What are 5 facts about Afghanistan?
What is Afghanistan famous for?
What is the cultural truth of Afghanistan?
What are the sad facts about Afghanistan?
Afghanistan Country Profile
10 Things You Did not Know About Afghanistan
10 Interesting Facts About Afghanistan
Matters related to Afghanistan
Information about the war in Afghanistan
Information about life in Afghanistan
25 Interesting Facts About Afghanistan
History of Afghanistan
Population of Afghanistan
Afghanistan is the 37th most populous country in the world
With a population of around 40-million, it is the 37th most populous country in the world. Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. About 10% of the population lives in Kabul. The official languages of Afghanistan are Pashto and Dari.
What are 5 facts about Afghanistan?
Afghanistan Country Profile - National Geographic Kids
Fast facts
Official name: Islamic Republic of Afghanistan.
Capital: Kabul.
Population: 34,940,837 people.
Official languages: Dari (Afghan Persian), Pashto.
Currency: Afghani.
Area: 251,823 sq mi (652,230 sq km)
What is Afghanistan famous for?
Afghanistan is well known for its fine fruits, especially pomegranates, grapes and extra-sweet jumbo-sized watermelons.
What is the cultural truth of Afghanistan?
Afghanistan - Culture, Traditions, Customs Britannica Afghans celebrate their religious or national festival days, especially weddings, with public dances. Open air Atan dance performances are a feature of Afghan life. It became the national dance of the Pashtuns and then the entire country.
What are the sad facts about Afghanistan?
Decades of ongoing conflict, political instability, drought and economic chaos have left Afghanistan as one of the poorest and most unstable countries in the world. Afghanistan is the world second largest source of refugees, with 2.5 million people displaced outside the country - and possibly more who are unregistered.
What you should know about Afghanistan?
Afghanistan is the 37th most populous country in the world.
Afghanistan is the 41st largest country in the world.
There are no public Christian churches in Afghanistan.
The world oldest oil paintings are in Afghanistan.
Afghanistan is the largest opium producing country in the world.
What is the famous food of Afghanistan?
Escape to Kabul
The national dish of Afghanistan is Kabuli Palao, a rice dish cooked with raisins, carrots, almonds and lamb or beef.
What is the nickname of Afghanistan?
Popularly referred to as the graveyard of empires, this land has historically been home to various peoples and witnessed numerous military campaigns including Persians, Alexander the Great, Mauryan Empire, Arab Muslims, Mongols, British, Soviets. Union, and a US-led coalition.
Is Afghanistan prosperous?
It is headquartered in Kabul with regional offices in other parts of the country. Afghanistan has more than 1,400 mineral fields, including barite, chromite, coal, copper, gold, iron ore, lead, natural gas, petroleum, precious and semi-precious stones, salt, sulphur, lithium, talc and zinc, among others. minerals
What is the national animal of Afghanistan?
snow leopard
National symbol of Afghanistan
title symbol
The national animal is the snow leopard
The national bird is the Golden Eagle
The national dog is the Afghan Hound
The national flower is the tulip
What is the symbol of Afghanistan?
Above the symbol of Afghanistan is the Shahada inscription in Arabic. Below it is the image of a mosque with a mihrab and mimbar or pulpit. Attached to the mosque are two flags, which stand for the flag of Afghanistan.
What is the old name of Afghanistan?
Is Mahabharata connected with Afghanistan?
Afghanistan was once not what we see it today, says the study. The fact that it was once known as Gandhara and that it still has a city known as Kandahar confirms the fact. According to experts, the kingdom of Gandhara covered parts of present-day northern Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan.
What is the new name of Afghanistan?
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the junction of Central Asia and South Asia.
What is the national fruit of Afghanistan?
List of National Fruits
The common name of the country is the scientific name
Pomegranate Punica granatum of Afghanistan
Albania cherry Prunus avium
Algeria Date Phoenix Dactylifera
Angola palm Borassus flabellifer
What is the heart of Afghanistan?
Heart of Afghanistan American Voices
Afghanistan Heart Project features four Afghan musicians; Ahmed Fanus on vocals and harmonium and his two sons Ilham on piano and Mehran on violin, Sohail Karimi on tabla.
What is the largest city in Afghanistan?
Kabul
Kabul (pronounced KAH−bool) is the capital city of Afghanistan. It had an estimated population of 3.573 million people in 2009. At an elevation of 5,895 feet/1,797 meters, it is Afghanistan largest city, as well as its economic and cultural center.
What does afghan mean?
A person born or residing in Afghanistan
Afghan Af-Agan. 1.: A person born or living in Afghanistan. 2. Not capitalized: A blanket or shawl made of knitted or crocheted colored wool.
What is the nickname of Kabul?
Before the Soviet invasion of 1979 and the rise of radical Islam, Kabul natives and urbanites -- known as Kabulis -- lived in their safe and modern city. As Afghanistan developed between the 1930s and 1970s, Kabul showcased the country progress and earned the nickname "Paris of Central Asia".
What is afghan unisex name?
Examples of gender-neutral Afghan names include: Gul (meaning "flower"), Lal, Sultan, Taj, and Shaista.
What is the name of the flag of Afghanistan?
The national flag of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (Pashto: د افغانستان براغ; Dari: پرکم افکانستان), adopted on 15 August 2021 following the victory of the Taliban in the 2001–2021 war, features a white field inscribed with a black Shahada.
Is Afghanistan a Shia country?
Observers estimate that 80 percent of the population is Sunni Muslim, 19 percent Shia Muslim, and other religious groups less than 1 percent of the population.
Is Afghan food spicy?
Afghans do not like their food too spicy or too hot, yogurt is used as a dressing, topping or accompaniment. Lamb and chicken are widely enjoyed, Afghani lamb kebabs are a very popular street food.
What are the 7 dry fruits of Afghanistan?
Haft mewa does not have to contain exactly seven fruits, but Ahmadi says it usually includes most or all of these ingredients: pistachios, almonds, walnuts, raisins, dried apricots, sultanas, black currants, lotus fruit, soft pitted apricots, and cashews.
Afghanistan History, Maps, Flags, Capitals, Population
Afghanistan, a landlocked country in South Asia, has a rich and complex history. Here is a brief overview:
History: Afghanistan has been inhabited for thousands of years, the region has seen the rise and fall of various civilizations. It is a crossroads of cultures connecting the Middle East, Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent. In recent history, Afghanistan was part of the Persian Empire, the Mauryan Empire, the Greek Empire under Alexander the Great, and the Kushan Empire. In modern times, it was ruled by various dynasties, including the Durrani Empire. In the 20th century, Afghanistan experienced significant political turmoil, including the Soviet invasion in 1979 and subsequent civil war.
Map: Afghanistan is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and Tajikistan to the north, and China to the northeast. Its geography is characterized by rugged mountains, plains and deserts.
Flag: The flag of Afghanistan consists of three equal vertical bands of black, red and green with the national emblem in the center. The symbol features a mosque with its mihrab facing Mecca, surrounded by sheaves of wheat. Above the mosque are the words "Allahu Akbar" (God is great) in Arabic script.
Capital: Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. It has been an important cultural and economic center throughout the country history.
Population: As of my last update in January 2022, the population of Afghanistan was estimated to be around 38 million people. However, population figures may change due to factors such as conflict, migration and natural disasters.
It is important to note that Afghanistan faces significant challenges, including political instability, conflict and humanitarian crisis. The situation in the country may have evolved since my last update, so it is a good idea to consult the latest sources for the latest information.
Afghanistan Country Profile
Here is a brief profile of Afghanistan:
Official name: Islamic Republic of Afghanistan
Capital: Kabul
Official Languages: Pashto and Dari (Persian)
Government: Single President Islamic Republic
President: The current President (as of my last update) was Ashraf Ghani.
Population: About 38 million (as of my last update)
Area: About 652,864 square kilometers (252,072 sq mi)
Currency: Afghan Afghani (AFN)
GDP (Gross Domestic Product): Afghanistan economy is primarily agricultural, with agriculture employing a significant portion of the population. It has natural resources such as natural gas, petroleum, coal, copper, talc and other minerals.
Religion: Islam is the main religion, the majority of the population is Sunni Muslim. There are also small communities of Shia Muslims and other religious minorities.
Ethnic Groups: Afghanistan is ethnically populated by Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, Uzbeks and other ethnic groups.
History: Afghanistan has a long and complex history, marked by various empires, invasions and periods of conflict. It has been the crossroads of cultures and civilizations for centuries.
Recent Developments: Afghanistan has faced significant challenges in recent decades, including conflict, political instability and economic hardship. The withdrawal of international troops and the resurgence of the Taliban have profound implications for the country future.
This profile provides a basic overview of Afghanistan, but the situation in the country is dynamic and subject to change. For the most up-to-date information, it is essential to consult recent news sources and reports.
Covering an area of 652,864 square kilometers (252,072 sq mi), the country is mainly mountainous with plains in the north and southwest, which are divided by the Hindu Kush mountain range. Kabul is the country largest city and serves as its capital.
10 Things You Did not Know About Afghanistan
Here are ten lesser-known facts about Afghanistan:
Birthplace of Zoroastrianism: The region that is now Afghanistan is believed to be the birthplace of Zoroastrianism, one of the world oldest monotheistic religions, dating back more than 3,000 years.
Ancient Buddhist Sites: Afghanistan was once home to a thriving Buddhist civilization, with notable sites such as the Bamiyan Buddha, a giant statue carved into the mountains of the Bamiyan Valley. Sadly, they were destroyed by the Taliban in 2001.
Melting Pot of Cultures: Afghanistan has been a cultural crossroads influenced by various civilizations including Persian, Greek, Indian and Central Asian cultures for centuries.
World Largest Refugee Population: Afghanistan has been experiencing decades of conflict and instability, resulting in one of the world largest refugee populations. Millions of Afghans have sought refuge in neighboring countries and beyond.
Kite flying tradition: Kite flying is a popular tradition in Afghanistan, especially during spring. Kite fighting, where participants try to cut each other kites, is a cherished pastime.
National Sport: Buzkashi: Buzkashi is the national sport of Afghanistan, also popular in Central Asian countries. In it, players on horseback compete to catch a goat carcass and carry it to the goal.
Rich Poetry Tradition: Afghanistan has a rich tradition of poetry, with poets like Rumi and Khushal Khan Khattak having a lasting influence on Persian and Pashto literature.
Afghan Hound: The Afghan Hound, a dog breed known for its elegance and distinctive appearance, originated in Afghanistan. It was historically used for hunting in the region.
Lapis Lazuli: Afghanistan is famous for its lapis lazuli, a deep blue semi-precious stone prized for its beauty. The country has been a major source of lapis lazuli for thousands of years.
Cuisine: Afghan cuisine is varied and delicious, with Kabuli pulao (a rice dish with meat and raisins), mantu (dumplings) and kebabs being popular. Tea, often spiced with cardamom, is a common drink.
These facts highlight Afghanistan cultural, historical and natural richness, giving a glimpse of its diverse heritage beyond the headlines of conflict and unrest.
10 Interesting Facts About Afghanistan
Here are ten interesting facts about Afghanistan:
Hilly Land: Afghanistan is a landlocked country dominated by rugged mountains. In fact, it is home to some of the highest peaks in the world, including Noshak, which stands at 7,492 meters (24,580 ft) above sea level.
Babur Gardens: The Bagh-i Babur (Garden of Babur) in Kabul is one of the oldest surviving gardens in the world, dating back to the 16th century. It was commissioned by Emperor Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire.
World Best Pomegranates: Afghanistan is famous for producing world best pomegranates. The fruit is not only a staple of Afghan cuisine, but is also a significant export.
Silk Road Crossroads: Afghanistan was an important crossroads along the ancient Silk Road, facilitating trade and cultural exchange between East and West for centuries.
Astronomical heritage: The city of Herat in western Afghanistan was once a center of Islamic astronomy and mathematics in the Middle Ages. It was home to influential scholars like al-Biruni.
Traditional Carpets: Afghan rugs, also known as Afghan rugs or Afghan carpets, are highly prized for their quality and craftsmanship. They often feature intricate designs and are hand-woven by skilled artisans.
Cultural Diversity: Afghanistan is ethnically and linguistically diverse, with Pashtun, Tajik, Hazara, Uzbek and other groups coexisting. This diversity is reflected in its cuisine, traditions and customs.
Loya Jirga: The Loya Jirga or Grand Assembly is a traditional Afghan institution where tribal elders, community leaders and other representatives come together to make important decisions. It has played an important role in Afghan politics and governance.
Saffron production: Afghanistan is emerging as a major producer of saffron, the world most expensive spice by weight. Saffron cultivation has become an important source of income for Afghan farmers.
Hospitality: Afghans are known for their hospitality and kindness towards guests. It is customary for visitors to be treated with great respect and offered tea or snacks as a welcome gesture.
These facts provide a glimpse into Afghanistan diverse culture, rich history and natural beauty, highlighting its significance on the world stage beyond the lens of conflict and unrest.
Matters about Afghanistan
One interesting thing about Afghanistan may be its efforts at cultural preservation amid decades of conflict and political instability. Here an outline of what you can explore:
Introduction to Afghanistan Cultural Heritage: Begin by introducing Afghanistan rich cultural heritage, including its ancient history, diverse ethnic groups, languages, traditions and art forms.
Impact of Conflict on Cultural Heritage: Discuss how decades of conflict, including invasions, civil war, and Taliban rule, have endangered Afghanistan cultural heritage. Cite specific examples of cultural destruction, such as attacks on the Buddha of Bamiyan and historical sites and monuments.
Efforts for Preservation: Explore the efforts of Afghan authorities, international organizations, and local communities to preserve and protect Afghanistan cultural heritage. These may include initiatives such as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, museum conservation projects, and efforts to document and protect cultural heritage.
The Role of Cultural Diplomacy: Examines how Afghanistan uses its cultural heritage as a tool for diplomacy and international engagement. This may involve cultural exchanges, exhibitions and collaborations with other countries to promote Afghan art, music, literature and cuisine.
Challenges and Opportunities: Discuss the challenges faced in preserving Afghanistan cultural heritage, including ongoing conflict, resource scarcity, looting, and illegal trafficking of artifacts. Explore potential opportunities for sustainable development and cultural revitalization.
Case Studies: Provide case studies of successful conservation efforts or cultural revitalization projects in Afghanistan. Highlight the role of local communities, NGOs and international partnerships in these efforts.
Future Prospects: Conclude by discussing the importance of preserving Afghanistan cultural heritage for future generations and the potential impact on tourism, economic development, and national identity. Consider the role of education, technology and public awareness in preserving Afghanistan cultural heritage.
By focusing on Afghanistan cultural heritage, you can discuss a topic that not only highlights the country rich history and heritage but also the resilience of its people in the face of adversity.
Information about the war in Afghanistan
A remarkable fact about the war in Afghanistan is its longevity, making it one of the longest-running conflicts in modern history. Here some context:
The war in Afghanistan, often called the Afghan war or the war on terror, began in 2001 after the September 11 attacks on the United States. The goal of the US-led invasion of Afghanistan was to topple the Taliban regime, which had harbored Osama bin Laden and al-Qaeda, the terrorist group responsible for the attacks.
Since then, the conflict has evolved into a complex and protracted war involving multiple actors, including Afghan government forces, international coalition troops, insurgent groups such as the Taliban and ISIS-Khorasan, and various local militias.
Afghanistan remains mired in violence and instability despite efforts to stabilize the country and build democratic institutions. The war has exacted a heavy toll on Afghan civilians, with thousands killed or injured and millions displaced from their homes.
The conflict has also incurred significant human, financial, and geopolitical costs for the United States and its allies, leading to debate over the effectiveness and sustainability of military intervention in Afghanistan.
As of my last update in January 2022, efforts to reach a political settlement and end the war continue, but the situation is fluid and the future uncertain. The war in Afghanistan serves as a stark reminder of the complexities and challenges involved in dealing with conflict and extremism in the 21st century.
Information about life in Afghanistan
Despite the challenges posed by decades of conflict and instability, there are many facts about life in Afghanistan that highlight the resilience and spirit of its people. Here is one:
Strong sense of community and hospitality: Afghan society is characterized by a strong sense of community and hospitality. Families and communities often come together to support each other in times of need, whether in celebration, mourning or everyday struggles. Hospitality towards guests is deeply embedded in Afghan culture, where visitors are often greeted warmly and offered tea or food as a sign of respect and friendship.
This sense of community extends beyond immediate family ties, with neighbors, friends and even strangers often stepping up to help one another. It reflects the importance of social bonds and solidarity in Afghan society, providing a source of strength and resilience in the face of adversity.
This aspect of life in Afghanistan demonstrates the enduring cultural values and traditions that have sustained communities throughout the country turbulent history. Despite the challenges they face, Afghans continue to draw on their collective resilience and sense of solidarity to navigate the complexities of daily life.
25 Interesting Facts About Afghanistan
Here are 25 interesting facts about Afghanistan:
Land of the Afghans: The name "Afghanistan" means "land of the Afghans", derived from the Pashto word "Afghan", which refers to the country largest ethnic group, the Pashtuns.
Crossroads of Asia: Afghanistan has historically been a crossroads of trade and culture, connecting South Asia, Central Asia, the Middle East and China.
Diverse Geography: Afghanistan landscape is varied, from mountains to deserts to fertile valleys. It is home to some of the highest mountains in the world, including the Hindu Kush range.
Birthplace of Buddha: The Bamiyan region of Afghanistan is famous for the Buddhas of Bamiyan, giant statues carved into the mountains. They were built in the 6th century and destroyed by the Taliban in 2001.
Saffron production: Afghanistan is one of the world largest producers of saffron, a highly prized spice derived from the crocus flower.
Origins of the Taliban: The Taliban emerged in the early 1990s amid the chaos of the Afghan civil war. The group gained control of much of Afghanistan in the late 1990s before being ousted by the US-led invasion in 2001.
Ethnic Diversity: Afghanistan is home to various ethnic groups including Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, Uzbeks, Aimaks, Turkmen, Baloch and others.
Strategic Location of Kabul: The capital city of Kabul has been an important center of trade, culture and politics for centuries due to its strategic location along the Silk Road.
Delicious Cuisine: Afghan cuisine is known for its rich flavors and use of spices. Popular dishes include Kabuli pulao (rice with meat and raisins), mantu (dumplings) and kebabs.
A melting pot of cultures: Afghanistan history has been shaped by various civilizations, including Persian, Greek, Buddhist, Islamic and Soviet influences.
National Sport: Buzkashi: Buzkashi is Afghanistan national sport, where players on horseback compete to catch a goat carcass and carry it to a target.
Hospitality: Afghans are known for their hospitality and kindness towards guests, tea is a common gesture of welcome.
Lapis Lazuli: Afghanistan is famous for its lapis lazuli, a deep blue semi-precious stone prized for its beauty. The country has been a major source of lapis lazuli for thousands of years.
Literary Tradition: Afghanistan has a rich literary tradition, with poets like Rumi and Khushal Khan Khattak having a lasting influence on Persian and Pashto literature.
Silk Road Link: Afghanistan was an important link along the ancient Silk Road, facilitating trade between East and West.
Traditional Music: Afghan music encompasses a wide range of styles, including classical, folk, and traditional Pashto and Persian music.
Archaeological Sites: Afghanistan has many archaeological sites, including the ancient city of Balkh, which is believed to be one of the oldest cities in the world.
National symbol: The national symbol of Afghanistan consists of a mosque with its mihrab facing Mecca, surrounded by sheaves of wheat.
Handicrafts: Afghan artisans produce a variety of handicrafts, including carpets, ceramics, jewelry and embroidery, which are admired for their quality and craftsmanship.
Zoroastrian Tradition: Afghanistan is believed to be the birthplace of Zoroastrianism, one of the world oldest monotheistic religions.
Cultural Celebrations: Afghan culture is celebrated through various festivals and holidays including Nowruz (Persian New Year), Eid-ul-Fitr and Eid-ul-Azha.
Ancient Trade Routes: The Wakhan Corridor, a narrow strip of land in northeastern Afghanistan, once served as an important trade route between Central Asia and South Asia.
Nomadic Tribes: Afghanistan is home to several nomadic tribes, such as the Kuchi people, who migrate seasonally with their herds.
Architectural Heritage: Afghanistan boasts of a rich architectural heritage, with notable structures such as the Minaret of Jam, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Challenges and Resilience: Despite facing significant challenges, including conflict, poverty and natural disasters, the Afghan people have demonstrated remarkable resilience and perseverance.
These facts provide a glimpse into the diverse and fascinating country of Afghanistan, highlighting its rich history, culture and contributions to the world.
History of Afghanistan
Afghanistan history is long and complex, marked by periods of empire, invasion, and cultural development. Here an overview:
Ancient Afghanistan: The region of present-day Afghanistan has been inhabited since ancient times, with evidence of human presence dating back to the Paleolithic era. Afghanistan was part of several ancient civilizations, including the Achaemenid Empire, the Mauryan Empire, and the Graeco-Bactrian Empire.
Buddhist Period: Afghanistan was a major center of Buddhism from the 3rd century BC to the 7th century BC. The region had several Buddhist monastic centers and monumental statues such as the Buddha of Bamiyan.
Islamic Conquest: Afghanistan was conquered by Arab Muslims in the 7th century AD during the Islamic expansion. Islam gradually became the dominant religion and Afghanistan became part of various Islamic caliphates and empires.
Ghaznavid and Ghurid Empires: Afghanistan was ruled by several Islamic dynasties, including the Ghaznavid and Ghurid Empires, which were known for their patronage of literature, art and architecture.
Mongol invasion: In the 13th century, Afghanistan was invaded by the Mongols under Genghis Khan, causing widespread destruction and depopulation. The region later became part of the Timurid Empire.
Mughal rule: Afghanistan was incorporated into the Mughal Empire in the 16th century under Emperor Babur, who established the city of Kabul as the imperial capital. The region experienced a period of relative stability and prosperity under Mughal rule.
Durrani Empire: In the 18th century, Ahmad Shah Durrani, also known as Ahmad Shah Abdali, established the Durrani Empire, which encompassed present-day Afghanistan, Pakistan, and parts of Iran and India. Kabul became the capital of the empire.
British influence and the Anglo-Afghan War: In the 19th century, Afghanistan became a battleground for imperial rivalry between the British Empire and the Russian Empire, leading to the Anglo-Afghan War. Despite British attempts to control Afghanistan, the country maintained its independence.
20th century: The 20th century saw significant political changes in Afghanistan, including the establishment of a constitutional monarchy in 1923 and a period of modernization and reform. However, internal unrest and external pressure, including Soviet influence, led to political upheaval.
Soviet invasion and civil war: In 1979, the Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan to support the communist government against rebel groups. The Soviet occupation led to a protracted conflict and a devastating civil war that lasted nearly a decade.
Taliban rule: In the 1990s, the Taliban, a militant Islamist group, emerged and seized control of much of Afghanistan, imposing strict Islamic laws. The Taliban rule was characterized by human rights abuses and cultural repression.
Post-9/11 era: After the September 11, 2001 attacks on the United States, a US-led coalition invaded Afghanistan to overthrow the Taliban regime and destroy terrorist networks. Afghanistan has since experienced a protracted conflict and ongoing efforts to establish stability, democracy and economic development.
This overview provides a broad outline of Afghanistan history, highlighting its rich cultural heritage, periods of prosperity, and enduring resilience in the face of adversity.
Population of Afghanistan
As of my last update in January 2022, the population of Afghanistan was estimated to be around 38 million people. However, population figures may change due to factors such as conflict, migration and natural disasters. Afghanistan is demographically a young country, with a significant portion of its population under the age of 25. The population is ethnically diverse, with Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, Uzbeks, Aimaks, Turkmens, Balochs and others making up its population. Due to ongoing conflict and instability, Afghanistan faces significant challenges in healthcare, education and economic development, which have affected population growth and the quality of life of its citizens.